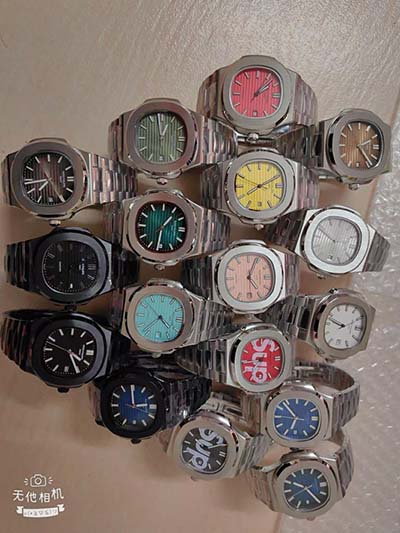
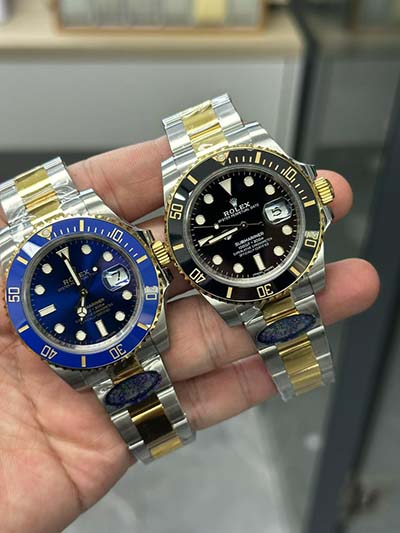
raid lv 3 | level 3 raid power sandwich raid lv 3 RAID levels explained. RAID levels can be broken into three categories: . GOLD ARDILLON BUCKLE. $2,020.00. Item Unavailable. Watches. Traditional Watches. My LV Tambour. Gold Ardillon Buckle. LOUIS VUITTON Official USA site - Discover our latest GOLD ARDILLON BUCKLE, available exclusively on louisvuitton.com and in Louis Vuitton stores.
0 · raid with 3 disks
1 · raid 3 vs 5
2 · raid 3 vs 4
3 · raid 3 diagram
4 · raid 3 bit level
5 · raid 3 and 4 difference
6 · level 3 raid power sandwich
7 · difference between raid 3 and 4
Services | LV Nails & Spa of Henderson, Nevada 89052 | Gel Manicure, Dipping Powder, Organic Pedicure, Acrylic, Waxing. Our Services. " Price may subject to change without notice " Manicures & Pedicures. Classic Mani $25+. Classic Pedi $35+. Deluxe Pedi (OPI) $50+. Royal Pedi (OPI) $65+. Pearl/Volcano Pedi $65+. Island Oasis Pedi $67+.Throughout the years, different definitions have surfaced on the internet, contemplating the inner meaning of “Mnbvcxzlkjhgfdsapoiuytrewq.”Two good examples for sites that feature these definitions are Urban Dictionary and definition-of.com.. In 2018, a short, 1 second-long video was updated on YouTube by the channel Cmanflip, that .
Raid 3: Bit-Level Striping with Dedicated Parity Like RAID 2, RAID 3 is rarely .

hublot world cup edition 2015 price in india
RAID 3 is also similar to RAID 5, except this solution requires a dedicated parity . RAID levels explained. RAID levels can be broken into three categories: .RAID 3 (redundant array of independent disks 3) is a RAID configuration that uses a parity disk .

raid with 3 disks
This level uses RAID 0 and RAID 1 for providing redundancy. Stripping of data is . RAID level 5 – Striping with parity. RAID 5 is the most common secure RAID .
If your business is considering implementing a RAID array, learn more about .RAID levels 2, 3, and 4 are theoretically defined but not used in practice. There are some more .RAID 3, which is rarely used in practice, consists of byte-level striping with a dedicated parity disk. One of the characteristics of RAID 3 is that it generally cannot service multiple requests simultaneously, which happens because any single block of data will, by definition, be spread across all members of the set and will reside in the same . Raid 3: Bit-Level Striping with Dedicated Parity Like RAID 2, RAID 3 is rarely used in practice. This RAID implementation utilizes bit-level striping and a dedicated parity disk.
raid 3 vs 5
raid 3 vs 4
RAID 3 is also similar to RAID 5, except this solution requires a dedicated parity drive. RAID 3 is seldom used except in the most specialized database or processing environments, which can.

RAID levels explained. RAID levels can be broken into three categories: standard, nonstandard and nested. Standard levels of RAID are made up of the basic types of RAID numbered 0 through 6. A nonstandard RAID level is set to the standards of a particular company or open source project.
RAID 3 (redundant array of independent disks 3) is a RAID configuration that uses a parity disk to store the information generated by a RAID controller and uses striping for storing the data. Because the parity information is on a separate disk, RAID 3 does not perform well when tasked with numerous small data requests.
This level uses RAID 0 and RAID 1 for providing redundancy. Stripping of data is performed before Mirroring. In this level the overall capacity of usable drives is reduced as compared to other RAID levels. If your business is considering implementing a RAID array, learn more about each of the major configurations to decide which would be best for your organization. This guide highlights the design of each of the most popular RAID configurations as well as their advantages and disadvantages. RAID levels explained.RAID levels 2, 3, and 4 are theoretically defined but not used in practice. There are some more complex layouts: RAID 5E/5EE (integrating some spare space) and RAID DP but they are beyond the scope of this reference. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage method that integrates many disk drives into a single device to increase performance and offer redundancy. RAID 3 and RAID 4 are two RAID levels that employ .
Redundant Array of Independent Disks or RAID, is a data storage method that allows you to reduce data loss and improve read/write performance, by storing your information on multiple hard drives in what is called an array.RAID 3, which is rarely used in practice, consists of byte-level striping with a dedicated parity disk. One of the characteristics of RAID 3 is that it generally cannot service multiple requests simultaneously, which happens because any single block of data will, by definition, be spread across all members of the set and will reside in the same .
Raid 3: Bit-Level Striping with Dedicated Parity Like RAID 2, RAID 3 is rarely used in practice. This RAID implementation utilizes bit-level striping and a dedicated parity disk. RAID 3 is also similar to RAID 5, except this solution requires a dedicated parity drive. RAID 3 is seldom used except in the most specialized database or processing environments, which can.
RAID levels explained. RAID levels can be broken into three categories: standard, nonstandard and nested. Standard levels of RAID are made up of the basic types of RAID numbered 0 through 6. A nonstandard RAID level is set to the standards of a particular company or open source project.RAID 3 (redundant array of independent disks 3) is a RAID configuration that uses a parity disk to store the information generated by a RAID controller and uses striping for storing the data. Because the parity information is on a separate disk, RAID 3 does not perform well when tasked with numerous small data requests. This level uses RAID 0 and RAID 1 for providing redundancy. Stripping of data is performed before Mirroring. In this level the overall capacity of usable drives is reduced as compared to other RAID levels.
If your business is considering implementing a RAID array, learn more about each of the major configurations to decide which would be best for your organization. This guide highlights the design of each of the most popular RAID configurations as well as their advantages and disadvantages. RAID levels explained.
raid 3 diagram
RAID levels 2, 3, and 4 are theoretically defined but not used in practice. There are some more complex layouts: RAID 5E/5EE (integrating some spare space) and RAID DP but they are beyond the scope of this reference. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage method that integrates many disk drives into a single device to increase performance and offer redundancy. RAID 3 and RAID 4 are two RAID levels that employ .
raid 3 bit level
Trang web chính thức của LOUIS VUITTON tại Việt Nam - Khám phá thế giới của Louis Vuitton, cập nhật thông tin mới nhất, xem bộ sưu tập dành cho Nam và Nữ, tìm cửa hàng.
raid lv 3|level 3 raid power sandwich